5.2 Input and Output
| Goals: |
|
How Python opens will depend on the installation and version. The software includes an editor, called IDLE, that integrates with the Shell. If you don’t see IDLE, you can start it by selecting New File in the File menu. The editor allows for saving work and testing ideas, eliminating the need to type input into the Shell. Type the following into IDLE:
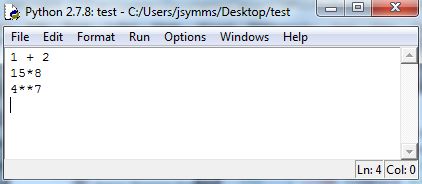
To run the code, select Run Module from the Run menu. Save the file, if necessary, and Python will automatically run the commands in a new or restarted Shell. But, Python will suppress the output of executed commands, unless you specify otherwise. One way to see the output is to use the print command, as follows:
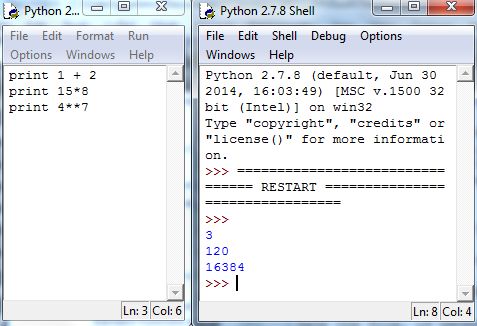
Thus far, we’ve seen two kinds of data types in Python: integers and floating-point numbers. A string in Python is a nonnumerical type, and is simply a string of characters inclosed by quotation marks. Examples of strings are "Angus is my name" and "2".1818It’s important to note that 2 and "2" are not equal in Python. The test of “equal” is discussed in Section 5.4.
If separated by commas, the command print will print multiple arguments. So we can beautify the output Figure 5.9 by adding some strings that gives context to the computations:
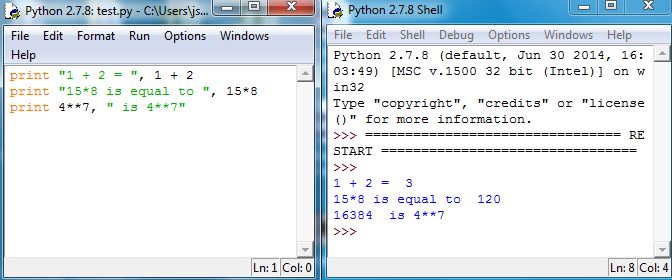
Another useful command is input, which allows prompting a user for input. The command takes an argument as a string. It then stores the response from the user as a numeric value, either floating-point (decimal number) or integer. When executed, input displays the string in the Shell, and returns1919“return” is explained in Section 5.3. the value entered by the user. Type the following in IDLE and then run in the Shell:
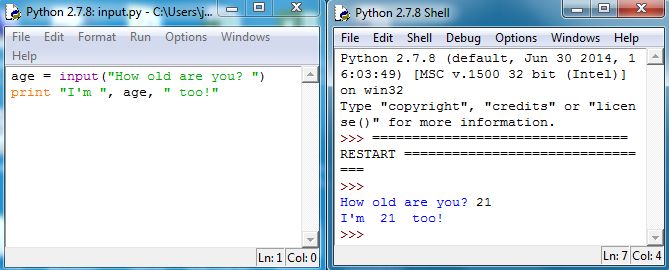
The command raw_input allows the user to prompt the user for input as well. However, it stores the input from the user as a string instead of a numeric value. Let’s try an alternative way of printing out a statement that relies on the value of a variable to be placed within the sentence. Type the following in IDLE and then run in the Shell:

Notice that we used to inform Python when a variable’s value will be placed. Also, notice that identifier immediately following the percent sign. This informs Python what type of variable is to be placed here. The following table shows what identifier goes with what variable type.
| %d | Integer |
|---|---|
| %f | Floating-point (decimal) |
| %s | String |
In our example, the variable age was of type integer and the variable year was of type string. Finally, notice that when more than one variable is to be placed in a printed statement, we can use %(var1, var2, …) to inform Python what variables are to be placed in their respectively places. That is, these variables will be placed in the order they are encountered in the sentence, as seen in the example above.
5.2.1 Exercises
-
1.
Answer the following as True or False.
-
(a)
A script file can be used to run more than one command at a time.
-
(b)
The print command always requires quotations.
-
(c)
The command input only takes an argument as a numeric value.
-
(d)
The command input requires parentheses around a string.
-
(e)
It is required that a space be placed before the ending quotation when using the commands input and raw_input.
-
(a)
-
2.
Create a script file that obtains and stores from the user their favorite color as a string, their birth year as a numeric value (integer), and their shoe size as a numeric value (floating-point). Then have it print out the statement, “I was born in (birth year). My favorite color is (color). My shoe size is (size).”