2.2 Redundancy Simulation
A slightly more complicated example:
-
A machine will stop working when a particular part called âGadgetâ breaks. In order to lengthen the time that the machine works, the machine has two Gadgets. One Gadget remains idle until the first breaks, at which point it activates. Suppose the probability that a Gadget breaks is each year, and suppose that when a Gadget breaks it does so only at the end of a year. What is the proportion of machines that run longer than 4 years?
As with the Family Planning example, there is a population of interest here: It is a collection of Y’s and N’s, where:33Note that the data type is different than in the Family Planning simulation, i.e., the Family Planning simulation yielded quantitative data (the number of girls in a family), but this simulation yields qualitative data, where the values are dichotomous.
There is a proportion of Y’s that we seek to estimate using a simulation.44 As with the Family Planning example, sufficient knowledge of probability theory can lead to an exact calculation. We can’t simulate a probability of using a standard 2-sided coin, but we can using three cards from a standard deck of playing cards:
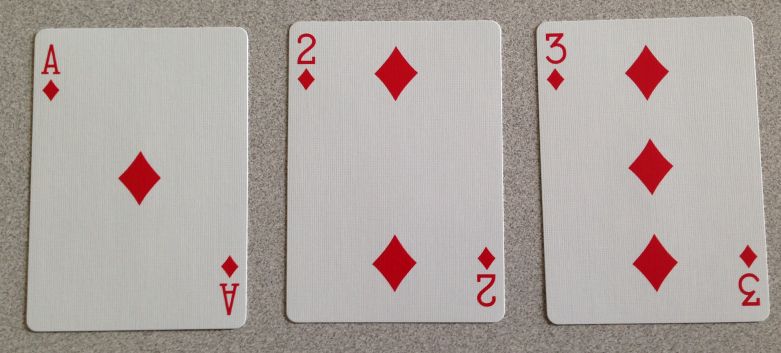
Designate the ace as ”the Gadget has failed.”
We can simulate whether a single machine last longer than four years as follows:
-
1.
Shuffle the cards and select one at random.
-
2.
Note that the machine is one year older. If the machine is 4 years old and the second gadget has not failed, then the machine lasted longer than four years, so output Y and go to Step 5. Otherwise, go to Step 3.
-
3.
If the ace was drawn, then the gadget failed. If this is the second gadget to fail, then output N and goto Step 5. If this is the first gadget to fail, make a note of that and go to Step 1.
-
4.
The gadget didn’t fail, so go to Step 1.
-
5.
Stop.
Repeating the algorithm above would simulate multiple machines, but the process shuffling the cards would quickly become tedious. The authors ran a simulation and got the following sample: The sample proportion of Y’s is
This simulation leads to some similar questions as with the Family Planning example:
-
•
How confident can we be that this is a good estimate for
-
•
What could we do to increase the level of confidence that is close to